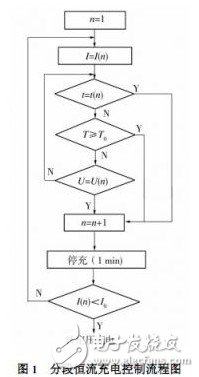
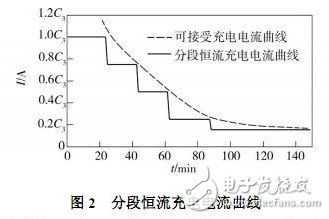
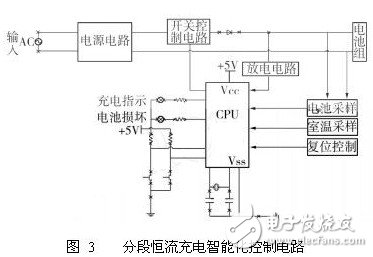
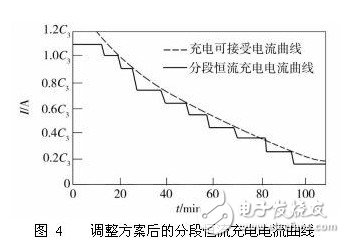
An electric vehicle is a vehicle that is driven by a vehicle power source and driven by a motor to meet the requirements of road traffic and safety regulations. As the impact on the environment is relatively small compared to traditional cars, its prospects are widely optimistic, but the current technology is not mature. Therefore, the rapid charging of batteries for electric vehicles in the process of marketing to the market is an important issue in the research and development of electric vehicles. Although many practical charging devices or commercial chargers have the functions of fast charging and balanced charging, they usually charge the battery according to a preset charging current. This method can't adjust the charging current according to the specific conditions of the battery charging process. In order to avoid overcharging, the set charging current is usually too small, so the charging time is still long, and the charging process is not adaptive. It is prone to overcharging, which is detrimental to the life of the battery. In order to achieve fast charging without affecting battery life, the key is to make the fast charging process adaptive, that is, to automatically adjust the charging current according to the actual state of the battery, so that it always maintains the critical value of the charging acceptable current. nearby. 1 Segmented constant current control for fast battery charging 1. 1 Choice of fast charging method Increasing the charging current increases the amount of active material recovered per unit time on the battery plate, and the charging time can be shortened, but excessive charging current can damage the battery. The acceptable charging current of the battery is limited and will decrease exponentially with the charging time. During the charging process of the battery, when the charging current curve is above the exponential function curve, the battery electrolyte will be subjected to a gassing reaction (overcharge), and vice versa, the charging time cannot be effectively shortened. The ideal battery fast charging process is that the charging current is always kept at the limit of the acceptable current for battery charging, that is, the charging current curve coincides with the charging acceptable current curve of the battery. This paper chooses a piecewise constant current charging method that is easy to implement. The key is to determine the appropriate segmented constant current charge termination judgment criteria, the number of constant current charge segments, and the constant current charge current values ​​at each stage. 1. 2 piece constant current charging control scheme To achieve automatic control of segmented constant current charging, the stage constant current charging termination determination parameter can select charging time, battery temperature and battery voltage. A large number of investigation and analysis and battery charging test results show that the single-parameter control method is difficult to achieve ideal segmented constant current charging control. The charging time parameter control method is simple, but the battery model is different, the charging starting state is different, and the required charging time is also different. If the charging time is used to control the end of the constant current charging, the battery may be overcharged or extended. . The advantage of the temperature parameter control method is that the battery over temperature protection can be realized, but due to the influence of the environment and the response time delay of the sensor, if the battery temperature parameter is used as the phase constant current charging termination judgment standard, the battery overcharge is easily caused. Voltage parameter control is considered to be a good phase constant current charge termination control method, but its shortcomings are obvious. For example, it is impossible to recognize the abnormal increase of the charging voltage caused by the vulcanization of the battery plate and the abnormal temperature that occurs during battery charging. Lit up, resulting in extended battery charging time or battery damage. In order to ensure that the actual state of charge of the battery can be detected under various conditions, and the ideal step-shaped charging current curve is realized, this paper combines three parameters of charging time, battery temperature and termination voltage as the basis for judging the termination of constant current charging in each stage. The control process is shown in Figure 1. T — battery temperature; T0—stop charging temperature; I0—minimum constant current charging current; t (n)—set charging time for nth constant current charging; I ( n)—setting of nth constant current charging Current value; U ( n) - setting of the nth constant current charging termination voltage segmentation After constant current charging is completed, a constant voltage charging is performed for a period of time to ensure that the battery is fully charged. The specific control strategies for the three control parameters are as follows. Time parameter control: According to the battery capacity and charging current, a certain period of constant current charging is preset. When the charging time reaches the set value, a signal is sent through the timer to end the constant current charging at this stage and automatically reduce the charging current. Small, enter the next constant current charging. Temperature parameter control: Set the maximum battery temperature when a constant current is charged to the acceptable current limit, and control the charging device according to the battery temperature detected by the temperature sensor. When the ambient temperature is low and the set maximum temperature of the battery is high, the temperature rise method is adopted. When the temperature rise of the battery reaches the set value, the temperature controller stops the charging device from charging until the temperature drops to an appropriate value. Automatically enter the next stage of constant current charging. Voltage parameter control: The absolute voltage of the battery can reflect the charging condition of the battery, and set a certain constant current charging to reach or close to the voltage of the acceptable current limit value. When the voltage reaches the set value, the charging device will automatically end this stage. Stream charging, going to the next stage. 1. 3 piece constant current charging test study According to the capacity of the battery, t ( n ), I ( n ) and U ( n) are initially set, and the charging test is performed. During the charging process, t ( n), I ( n) and U ( n) are adjusted according to actual conditions. Then proceed to the next charge test. The initial state of the battery for each charge is fully discharged at 3 h [10], and the data such as charging time, charging efficiency and battery temperature rise of each test are analyzed and compared, and the charging time is selected to be the shortest and the battery temperature rise is relatively small. The charging process, the segmented constant current charging current curve is shown in Figure 2. By analyzing the test results, the following conclusions can be drawn: (1) The gradient of the constant current value I ( n) of each segment should be appropriately reduced. Comparing the temperature rise of the battery and the several stages of constant current charging in which the constant current charging termination conditions are similar, it is found that the time for the full power is 5, the constant current charging time is the shortest, and the 4-stage constant current charging time is the shortest. Shorter than 3 cycles of constant current charging. Therefore, appropriately reducing the constant current value falling gradient (increasing the number of segments) of each segment makes the actual charging current curve closer to the charging acceptable current curve. (2) It is not effective to set the charging time t ( n) of each constant current section. It is easier to use the timer to control the charging time t ( n) of each constant current section. However, the optimum constant current is obtained because the charging state of the battery at the start of constant current charging is different or the charging acceptable current is reduced due to the battery capacity attenuation. The charging time also changes. Uncertainty in battery status makes it difficult to determine the optimal charging time. In the test, the following phenomena often occur: A certain constant current is charged to the set charging time, but the charging voltage is far from the termination voltage. At this time, the test selects to continue charging at the constant current value until the charging voltage reaches Termination voltage; the charging time of a certain constant current charging setting has not yet arrived, but the battery has a large amount of gassing (electrolyte "boiling"), and the charging voltage has been higher than the set termination voltage or the battery temperature has risen to a limit value. In this case, the charger will immediately stop the constant current charging and automatically transfer to the next stage. It can be seen that in the automatic control charging process, setting the charging time has little effect. (3) The battery temperature should not be used as a piecewise constant current charging control parameter alone. In theory, the battery temperature can be used as an automatic stop control parameter for constant current charging at each stage in the case where the state of charge of the battery is different at the start of charging. However, the error and hysteresis of the temperature sensor easily cause the battery to be overcharged, so it is not appropriate to use the battery temperature alone as the piecewise constant current charge termination control parameter. (4) The termination voltage parameter U ( n) is less adaptive to abnormal conditions. The termination voltage at different constant current values ​​is set as a control parameter, which can adapt to the state of charge of the battery when charging starts and the change of the acceptable current during charging of the battery, and the control is relatively simple. However, when the performance of the battery changes abnormally, the originally set termination voltage may be too high or too low, causing the battery to overcharge or prematurely lower the charging current and prolong the entire charging time. In addition, in different constant current charging stages, the degree of charge polarization inside the battery is also different, and the rate of increase of the charging voltage near the acceptable current limit is also significantly different, and it is necessary to accurately set various constant current charging states. It is very difficult to terminate the voltage. 2 Intelligent control of battery segmented constant current charging 2. 1 segmented constant current charging intelligent control scheme According to the results and analysis of the piecewise constant current charging test, the segmented constant current charging control scheme is adjusted as follows: (1) The phase constant current charging termination criterion is determined by the capacity gradient method. Through theoretical analysis and a large number of experimental studies, this paper considers that it is more appropriate to use the capacity gradient parameter dU / dC as the phase constant current charging termination criterion. According to the constant current charging characteristic curve of the battery, the charging termination capacity gradient parameter is determined. During the charging process, the controller samples the charging voltage with a set frequency, calculates the capacity gradient value under I ( n), and sets the charging value. The termination capacity gradient standard is compared, and it is judged based on the comparison result whether or not the current phase constant current charging is terminated. (2) Decrease the gradient of the constant current value of each segment. The initial constant current value I (1) of the battery is determined by experiments, and the current drop of the constant current charging is reduced. If the time to reach the charge termination capacity gradient value is short after the charge current is reduced (set a minimum charge time), the magnitude of the current drop is appropriately increased. (3) Set the battery temperature to the charging safety assurance control parameter. Set the maximum battery temperature limit. If the battery temperature reaches the limit during charging, stop charging immediately. When the battery temperature drops to the normal temperature, the charging current is appropriately reduced to continue charging until the constant current charging is completed. 2. 2 segmented constant current charging intelligent control circuit The segmented constant current charging intelligent control circuit is shown in Figure 3. The circuit is controlled by the CPU, which can detect the temperature of the rechargeable battery and the charging environment, time the battery charging, and sample the voltage and current of the battery during the charging process to control the segmented constant current charging process. 2. 3 Intelligent segmentation constant current charging test According to the adjusted segmented constant current charging scheme, the charging test is carried out. For the sake of comparison, the same type of battery used in the charging test before the scheme adjustment is used, and the initial state of charging is exactly the same. During the segmented constant current charging test after the adjustment scheme, the battery does not appear to be overheated and stops charging, the charging time is shortened, the charging efficiency is also improved, and the entire charging process is automatically performed according to the set program. Intelligent intervention is required without manual intervention. Segmented constant current charging makes the actual charging current curve of the battery close to the charging acceptable current curve, which is an effective method for realizing rapid charging of the battery. The capacity gradient method is used to determine the standard parameters of the constant current charging termination, reduce the gradient constant of the stepped constant current charging current, and supplement the protection control of stopping the charging when the battery temperature is too high, so that the intelligent fast charging control of the power battery can be realized. The test results show that this constant current charging control method can effectively shorten the charging time, improve the charging efficiency and prolong the battery life. Therefore, based on the theory of rapid battery charging, this paper conducts experimental research on the segmented constant current charging method, in order to realize the intelligent fast charging and balanced charging of the power battery.
Laser Radar contains LSPD Safety Laser Scanner and LS laser radar. LSPD safety laser scanner is type 3 with CE certificate. It can be used for agv safety and industrial area protection. LS laser radar is for agv guide. Many famous agv manufacturers has installed LS laser radar to guide their agvs. Our cooperating brand contains Quicktron, Mushiny, Aresbots, etc. Feedback from customers are quite posotive.
Laser Radar Laser Radar,Auto Guided Vehicle Guide Radar,Sick Laser Radar,Safety Scanner,Safety Laser Scanner,Ls Series Laser Radar Jining KeLi Photoelectronic Industrial Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdkelien.com